Contents
- 1 The Current State of AI in Finance: A Landscape in Rapid Evolution
- 2 The Optimistic Perspective: AI as a Force for Financial Innovation
- 3 The Pessimistic Perspective: Risks and Challenges of AI in Finance
- 4 Balanced Analysis: Navigating the AI Revolution in Finance
- 5 Future Outlook: The Next Decade of AI in Finance
- 6 Conclusion: Embracing the Future While Managing the Risks
The financial services industry stands at the precipice of a technological revolution. As we navigate through 2025, artificial intelligence (AI) has evolved from a futuristic concept to an indispensable tool reshaping every aspect of finance. From algorithmic trading to personalized banking experiences, AI is not merely augmenting traditional financial services—it’s fundamentally transforming how we think about money, risk, and financial relationships.
This transformation brings both unprecedented opportunities and significant challenges. While AI promises enhanced efficiency, better risk management, and democratized access to financial services, it also introduces new risks around bias, privacy, and systemic stability. As financial institutions invest an estimated $97 billion in AI by 2027, understanding both the optimistic potential and pessimistic concerns becomes crucial for stakeholders across the industry.
The Current State of AI in Finance: A Landscape in Rapid Evolution
The adoption of AI in financial services has accelerated dramatically in recent years. According to the World Economic Forum, financial services firms spent $35 billion on AI in 2023, with projections indicating growth to $97 billion by 2027. This represents one of the most heavily invested sectors in AI technology, reflecting the industry’s recognition of AI’s transformative potential.
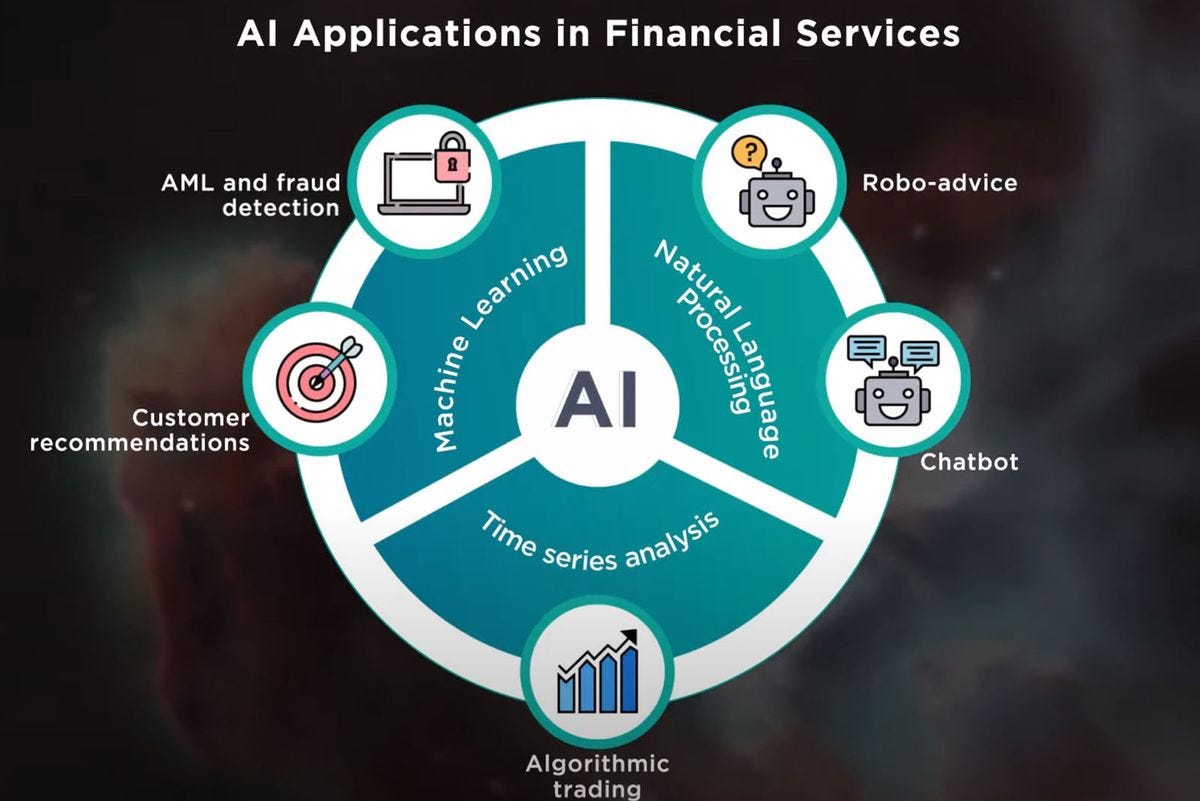
The current applications span across multiple domains:
Operational Efficiency: AI is automating 32-39% of tasks in banking, insurance, and capital markets, while augmenting 34-37% of workflows. This includes everything from document processing to customer service interactions.
Risk Management: Machine learning algorithms are revolutionizing fraud detection, credit scoring, and regulatory compliance. Real-time transaction monitoring can now identify suspicious patterns with unprecedented accuracy.
Customer Experience: AI-powered chatbots, personalized financial advice, and robo-advisors are making sophisticated financial services accessible to broader populations.
Trading and Investment: Algorithmic trading systems process vast amounts of market data to execute trades at speeds impossible for human traders, while AI-driven portfolio management optimizes investment strategies.
The Stanford HAI AI Index Report reveals that 78% of organizations, including those in finance, used AI in at least one business function in 2024, up from 55% in 2023. This rapid adoption reflects not just technological advancement but a fundamental shift in how financial institutions operate.
The Optimistic Perspective: AI as a Force for Financial Innovation
Enhanced Efficiency and Cost Reduction
The optimistic view of AI in finance centers on its ability to dramatically improve operational efficiency while reducing costs. Generative AI, in particular, is enabling financial institutions to automate complex tasks that previously required significant human intervention.
Process Automation: AI is streamlining back-office operations, from loan processing to regulatory reporting. Bank of America’s Erica chatbot, for example, has reduced call center costs by $300 million annually while improving customer satisfaction.
Predictive Analytics: Financial institutions can now predict market trends, customer behavior, and risk factors with remarkable accuracy. This enables proactive decision-making rather than reactive responses to market changes.
Document Processing: AI can analyze and extract information from complex financial documents in seconds, reducing processing time from days to minutes for loan applications and compliance reviews.
Democratization of Financial Services
AI is breaking down traditional barriers to financial services, making sophisticated tools accessible to previously underserved populations.
Alternative Credit Scoring: Machine learning algorithms can assess creditworthiness using non-traditional data sources, including social media behavior and transaction patterns. This enables lending to individuals without traditional credit histories.
Robo-Advisors: AI-powered investment platforms provide professional-grade portfolio management to retail investors at a fraction of traditional costs, democratizing wealth management services.
Financial Inclusion: In emerging markets, AI is enabling leapfrogging of legacy financial infrastructure. Companies like Nubank in Brazil and MoniePoint in Nigeria use AI to provide inclusive financial services to previously unbanked populations.
Superior Risk Management
AI’s ability to process vast amounts of data in real-time is revolutionizing risk management across the financial sector.
Fraud Detection: AI systems can identify fraudulent transactions in milliseconds, analyzing patterns across millions of transactions to detect anomalies that would be impossible for humans to spot.
Credit Risk Assessment: Machine learning models can evaluate loan applications more accurately than traditional methods, reducing default rates by up to 25% while expanding access to credit.
Market Risk Monitoring: AI enables continuous monitoring of market conditions, providing early warning systems for potential financial instability.
Innovation in Financial Products
AI is enabling the creation of entirely new financial products and services that were previously impossible.
Personalized Banking: AI analyzes individual spending patterns, financial goals, and life circumstances to provide tailored financial advice and product recommendations.
Dynamic Pricing: Insurance companies use AI to adjust premiums in real-time based on individual risk profiles and behavior patterns.
Algorithmic Trading: AI-driven trading strategies can identify market inefficiencies and execute trades with precision and speed that human traders cannot match.
Revenue Growth and Competitive Advantage
Approximately 70% of financial services executives expect AI to contribute directly to revenue growth. This comes through:
New Revenue Streams: AI enables the creation of new products and services, from AI-powered financial planning tools to sophisticated risk management solutions.
Customer Retention: Personalized experiences powered by AI increase customer satisfaction and loyalty, reducing churn rates.
Market Expansion: AI tools enable financial institutions to serve new market segments and geographic regions more effectively.
The Pessimistic Perspective: Risks and Challenges of AI in Finance
Algorithmic Bias and Fairness Concerns
Despite its potential benefits, AI in finance raises serious concerns about fairness and discrimination. Machine learning models can perpetuate or even amplify existing biases present in training data.
Credit Discrimination: AI systems trained on historical lending data may discriminate against certain demographic groups, perpetuating systemic inequalities in access to credit.
Employment Bias: AI-powered hiring tools in financial services may exhibit bias against certain candidates based on factors like gender, race, or socioeconomic background.
Insurance Redlining: AI-driven insurance pricing models may inadvertently create new forms of redlining, denying coverage or charging higher premiums to certain communities.
The challenge lies in the “black box” nature of many AI systems, making it difficult to identify and correct biases. Regulatory bodies like the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau have expressed concerns about AI systems that cannot provide clear explanations for their decisions.
Data Privacy and Security Vulnerabilities
The extensive use of personal and financial data in AI systems creates significant privacy and security risks.
Data Breaches: AI systems require vast amounts of sensitive financial data, creating attractive targets for cybercriminals. A single breach could expose millions of customers’ financial information.
Privacy Erosion: The granular analysis of financial behavior enabled by AI may erode customer privacy, creating detailed profiles of individuals’ spending habits, preferences, and life circumstances.
Third-Party Risks: Many financial institutions rely on third-party AI providers, creating additional vulnerabilities and potential points of failure in data security.
Systemic Risks and Market Instability
The widespread adoption of AI in finance creates new forms of systemic risk that could threaten financial stability.
Herding Behavior: If multiple institutions use similar AI models, they may make correlated decisions that amplify market volatility rather than stabilizing it.
Flash Crashes: AI-driven trading systems can execute thousands of trades in milliseconds, potentially causing rapid market crashes if algorithms react to false signals or unexpected events.
Concentration Risk: The dominance of a few AI providers in the financial sector could create single points of failure that affect multiple institutions simultaneously.
The Financial Stability Board has warned that AI could increase market correlations and systemic vulnerabilities, particularly through common model weaknesses that lead to correlated actions during market stress.
Cybersecurity Threats
AI introduces new attack vectors and amplifies existing cybersecurity risks.
Adversarial Attacks: Malicious actors can manipulate AI systems by feeding them carefully crafted inputs designed to cause incorrect decisions or outputs.
Deepfakes and Social Engineering: AI-generated deepfakes can be used to impersonate customers or executives, enabling sophisticated fraud schemes.
AI-Powered Attacks: Cybercriminals are using AI to create more sophisticated phishing emails, malware, and social engineering attacks targeting financial institutions.
Regulatory and Compliance Challenges
The rapid evolution of AI technology is outpacing regulatory frameworks, creating uncertainty and compliance challenges.
Regulatory Uncertainty: The lack of clear regulatory guidelines for AI in finance creates uncertainty for institutions trying to comply with existing laws while innovating with new technologies.
Cross-Border Complexity: Different jurisdictions have varying approaches to AI regulation, creating compliance challenges for global financial institutions.
Accountability Issues: When AI systems make decisions that result in harm or discrimination, it can be difficult to determine who is responsible—the institution, the AI vendor, or the algorithm itself.
Job Displacement and Workforce Disruption
AI’s ability to automate financial tasks raises concerns about widespread job displacement in the financial sector.
Automation of Routine Tasks: AI can perform many routine financial tasks more efficiently than humans, potentially eliminating jobs in areas like data entry, basic analysis, and customer service.
Skill Obsolescence: As AI capabilities advance, many traditional financial skills may become obsolete, requiring massive retraining efforts.
Inequality Amplification: The benefits of AI may accrue primarily to capital owners and highly skilled workers, potentially increasing inequality within the financial sector and society more broadly.
The reality of AI in finance lies somewhere between the utopian and dystopian visions. While AI offers tremendous potential for improving financial services, realizing these benefits requires careful attention to the associated risks and challenges.
The Importance of Responsible AI Development
The key to maximizing AI’s benefits while minimizing its risks lies in responsible development and deployment practices.
Explainable AI: Financial institutions must prioritize AI systems that can provide clear explanations for their decisions, particularly in areas like lending and insurance where fairness is crucial.
Bias Testing and Mitigation: Regular testing for bias and discrimination should be built into AI development processes, with ongoing monitoring to ensure fairness across different demographic groups.
Human Oversight: AI systems should augment rather than replace human judgment, particularly for high-stakes decisions that affect customers’ financial well-being.
Regulatory Evolution and Industry Standards
The financial services industry and regulators are working together to develop frameworks that enable innovation while protecting consumers and maintaining financial stability.
Risk-Based Regulation: Regulatory approaches are evolving toward risk-based frameworks that apply more stringent oversight to high-risk AI applications while allowing innovation in lower-risk areas.
Industry Collaboration: Financial institutions are collaborating on industry standards and best practices for AI development and deployment.
International Coordination: Global coordination on AI regulation is essential to prevent regulatory arbitrage and ensure consistent standards across jurisdictions.
The Role of Technology in Risk Mitigation
Ironically, AI itself may provide solutions to many of the risks it creates.
AI for AI Governance: AI systems can be used to monitor other AI systems for bias, errors, and security vulnerabilities.
Synthetic Data: AI-generated synthetic data can be used to train models while protecting customer privacy.
Federated Learning: This approach allows AI models to be trained on distributed data without centralizing sensitive information.
Future Outlook: The Next Decade of AI in Finance
Looking ahead to the next decade, several trends are likely to shape the evolution of AI in finance.
Technological Advancements
Quantum-AI Integration: The combination of quantum computing and AI could revolutionize financial modeling and risk assessment, enabling calculations that are currently impossible.
Agentic AI: AI agents that can act autonomously on behalf of customers could transform personal financial management, automatically optimizing investments, paying bills, and managing financial goals.
Multimodal AI: AI systems that can process text, images, voice, and other data types simultaneously will enable more sophisticated financial services and customer interactions.
Market Evolution
Embedded Finance: AI will enable the seamless integration of financial services into non-financial platforms, making financial transactions invisible and frictionless.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi): AI could play a crucial role in managing the complexity and risks of decentralized financial systems.
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs): AI will be essential for managing and securing digital currencies issued by central banks.
Societal Impact
Financial Inclusion: AI has the potential to bring sophisticated financial services to the world’s unbanked and underbanked populations.
Economic Efficiency: AI-driven financial systems could reduce transaction costs and improve capital allocation efficiency across the global economy.
New Forms of Value: AI may enable entirely new forms of value creation and exchange that we can barely imagine today.
Conclusion: Embracing the Future While Managing the Risks
The integration of AI into financial services represents one of the most significant technological transformations in the industry’s history. The potential benefits—enhanced efficiency, improved risk management, democratized access to financial services, and innovative new products—are substantial and compelling.
However, these benefits come with equally significant risks and challenges. Algorithmic bias, data privacy concerns, systemic risks, cybersecurity threats, and regulatory uncertainty all pose serious obstacles to the responsible deployment of AI in finance.
The path forward requires a balanced approach that embraces innovation while carefully managing risks. This means:
- Investing in responsible AI development practices that prioritize fairness, transparency, and accountability
- Developing robust governance frameworks that ensure human oversight and control over AI systems
- Collaborating across the industry to establish standards and best practices
- Working with regulators to develop appropriate oversight mechanisms
- Preparing the workforce for the changes that AI will bring
The financial institutions that succeed in the AI era will be those that can harness the technology’s power while maintaining the trust and confidence of their customers and regulators. This requires not just technical expertise but also a deep commitment to ethical principles and responsible innovation.
As we stand on the brink of this AI-driven transformation of finance, the choices we make today will determine whether AI becomes a force for greater financial inclusion, stability, and prosperity, or whether it exacerbates existing inequalities and creates new forms of systemic risk.
The future of finance is being written now, and it’s up to all stakeholders—financial institutions, regulators, technologists, and consumers—to ensure that this future serves the broader interests of society. The potential is enormous, but so is the responsibility to get it right.
The AI revolution in finance is not a distant future—it’s happening now. The question is not whether AI will transform financial services, but how we will shape that transformation to benefit everyone.
About This Analysis: This blog post synthesizes insights from leading financial institutions, regulatory bodies, academic research, and industry reports to provide a comprehensive view of AI’s impact on financial services. The analysis draws on data from the World Economic Forum, Financial Stability Board, Stanford HAI AI Index, and numerous other authoritative sources to present both optimistic and pessimistic perspectives on AI in finance.
Tags: #ArtificialIntelligence #Finance #FinTech #MachineLearning #RiskManagement #DigitalTransformation #BankingTechnology #AIEthics #FinancialServices #Innovation