Contents
- 1 The Current State of AI in Insurance
- 2 The Optimistic Perspective: AI as an Insurance Revolution
- 3 The Pessimistic Perspective: Risks and Challenges
- 4 Regulatory Landscape and Compliance Challenges
- 5 The Path Forward: Balancing Innovation and Responsibility
- 6 Future Predictions: Insurance in 2030 and Beyond
- 7 Conclusion: Navigating the AI-Powered Future of Insurance
Published: September 27, 2025
AI and digital transformation are reshaping the insurance landscape
The insurance industry stands at a pivotal moment in its evolution. As we navigate through 2025, artificial intelligence (AI) has emerged as the most transformative force reshaping how insurers assess risk, process claims, detect fraud, and serve customers. From automated underwriting that can approve policies in seconds to AI-powered chatbots handling millions of customer inquiries, the sector is experiencing a fundamental shift that promises both unprecedented opportunities and significant challenges.
This transformation is not merely about adopting new technology—it’s about reimagining the very essence of insurance. As McKinsey research indicates, AI could enable the industry to shift from a traditional “detect and repair” model to a revolutionary “predict and prevent” framework by 2030. But what does this mean for insurers, policyholders, and society at large?
The Current State of AI in Insurance
The adoption of AI in insurance has accelerated dramatically in recent years. According to industry surveys, over 90% of insurers are now using AI in some capacity, with applications spanning across all major operational areas. The technology has moved beyond experimental phases into core business functions, delivering measurable results that are reshaping competitive dynamics.

Claims processing automation through AI and machine learning
Current AI applications in insurance include:
- Automated Claims Processing: AI systems can now settle up to 60% of claims instantly with 96% accuracy
- Risk Assessment and Underwriting: Machine learning algorithms analyze vast datasets to improve prediction accuracy by up to 25%
- Fraud Detection: Advanced algorithms can reduce fraudulent claims by 30%, saving billions annually
- Customer Service: AI chatbots handle up to 74.2% of customer conversations, providing 24/7 support
- Personalized Pricing: Dynamic models adjust premiums based on real-time data and individual behaviors
The technology stack powering these applications includes machine learning, natural language processing, computer vision, and increasingly, generative AI. These tools are enabling insurers to process unstructured data, automate complex workflows, and deliver personalized experiences at scale.
The Optimistic Perspective: AI as an Insurance Revolution
Enhanced Efficiency and Cost Reduction
The optimistic view of AI in insurance paints a picture of unprecedented efficiency gains and cost reductions. Industry leaders report that AI-powered automation can reduce customer onboarding costs by 20-40% while increasing premium growth by 10-15%. Claims processing, traditionally a labor-intensive and time-consuming process, is being revolutionized with AI systems capable of reducing processing times by up to 80%.

Machine learning and data analytics transforming insurance operations
Consider the example of Lemonade’s AI system “Jim,” which processes 40% of claims instantly, often settling them in under three minutes. This level of automation not only reduces operational costs but also dramatically improves customer satisfaction by eliminating the frustration of lengthy claim processes.
Improved Risk Assessment and Pricing Accuracy
AI’s ability to analyze vast amounts of data from diverse sources is revolutionizing risk assessment. Traditional underwriting relied on limited historical data and broad demographic categories. Today’s AI systems can incorporate real-time data from IoT devices, social media, satellite imagery, and behavioral patterns to create highly accurate, individualized risk profiles.
In auto insurance, telematics data allows insurers to monitor actual driving behavior rather than relying on proxy indicators. This has led to more accurate pricing and the development of usage-based insurance models that reward safe driving with lower premiums. Similarly, in health insurance, wearable devices provide continuous health monitoring data that enables dynamic premium adjustments and proactive health interventions.
Enhanced Customer Experience and Personalization
The customer experience in insurance is being transformed through AI-powered personalization. Modern AI systems can analyze individual customer preferences, behaviors, and needs to deliver tailored products and services. This hyper-personalization extends beyond pricing to include customized policy recommendations, proactive risk management advice, and personalized communication preferences.
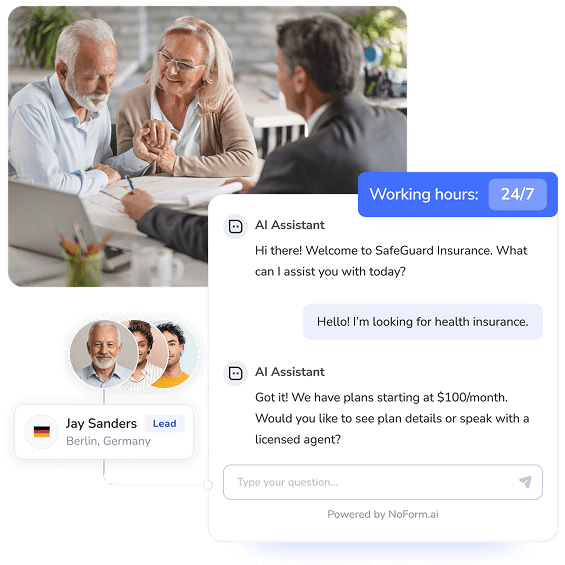
AI-powered chatbots revolutionizing insurance customer service
AI chatbots have evolved from simple rule-based systems to sophisticated conversational agents capable of handling complex inquiries. These systems provide 24/7 support, can communicate in multiple languages, and learn from each interaction to improve their responses. Companies like Allstate report that their AI assistant ABIE handles over 25,000 monthly inquiries, freeing human agents to focus on more complex cases.
Fraud Prevention and Security
AI’s pattern recognition capabilities make it exceptionally effective at detecting fraudulent activities. Machine learning algorithms can analyze millions of claims to identify subtle patterns that might indicate fraud, achieving detection rates that far exceed traditional methods. This not only saves money for insurers but also helps keep premiums lower for honest policyholders.
Advanced AI systems can detect various types of fraud, from staged accidents in auto insurance to inflated medical claims in health insurance. The technology’s ability to analyze multiple data sources simultaneously—including text, images, and behavioral patterns—makes it increasingly difficult for fraudsters to evade detection.
Innovation in Product Development
AI is enabling the development of entirely new insurance products and services. Parametric insurance, which pays out based on predefined triggers rather than actual losses, is becoming more viable thanks to AI’s ability to process real-time data from satellites, weather stations, and IoT sensors. This approach can provide faster payouts for events like natural disasters, reducing the financial impact on policyholders.
The Pessimistic Perspective: Risks and Challenges
Algorithmic Bias and Discrimination
Despite its promise, AI in insurance raises serious concerns about fairness and discrimination. AI systems trained on historical data may perpetuate or amplify existing biases, leading to unfair treatment of certain demographic groups. This is particularly concerning in insurance, where pricing decisions directly impact people’s access to essential coverage.
Studies have shown that AI systems can inadvertently discriminate based on factors like zip code, credit score, or occupation, which may serve as proxies for protected characteristics like race or socioeconomic status. For example, an AI model might unfairly penalize residents of certain neighborhoods by associating geographic data with higher risk, even without explicit discriminatory intent.
The legal landscape is evolving to address these concerns, with regulations like Colorado’s AI Act and the NAIC’s Model Bulletin requiring insurers to test for bias and ensure fair outcomes. However, the challenge of eliminating bias while maintaining predictive accuracy remains complex and ongoing.
Data Privacy and Security Vulnerabilities
The extensive use of personal data in AI systems creates significant privacy and security risks. Insurance AI systems process vast amounts of sensitive information, including health records, financial data, driving patterns, and behavioral information. This concentration of data makes insurers attractive targets for cybercriminals and raises concerns about how this information is collected, stored, and used.
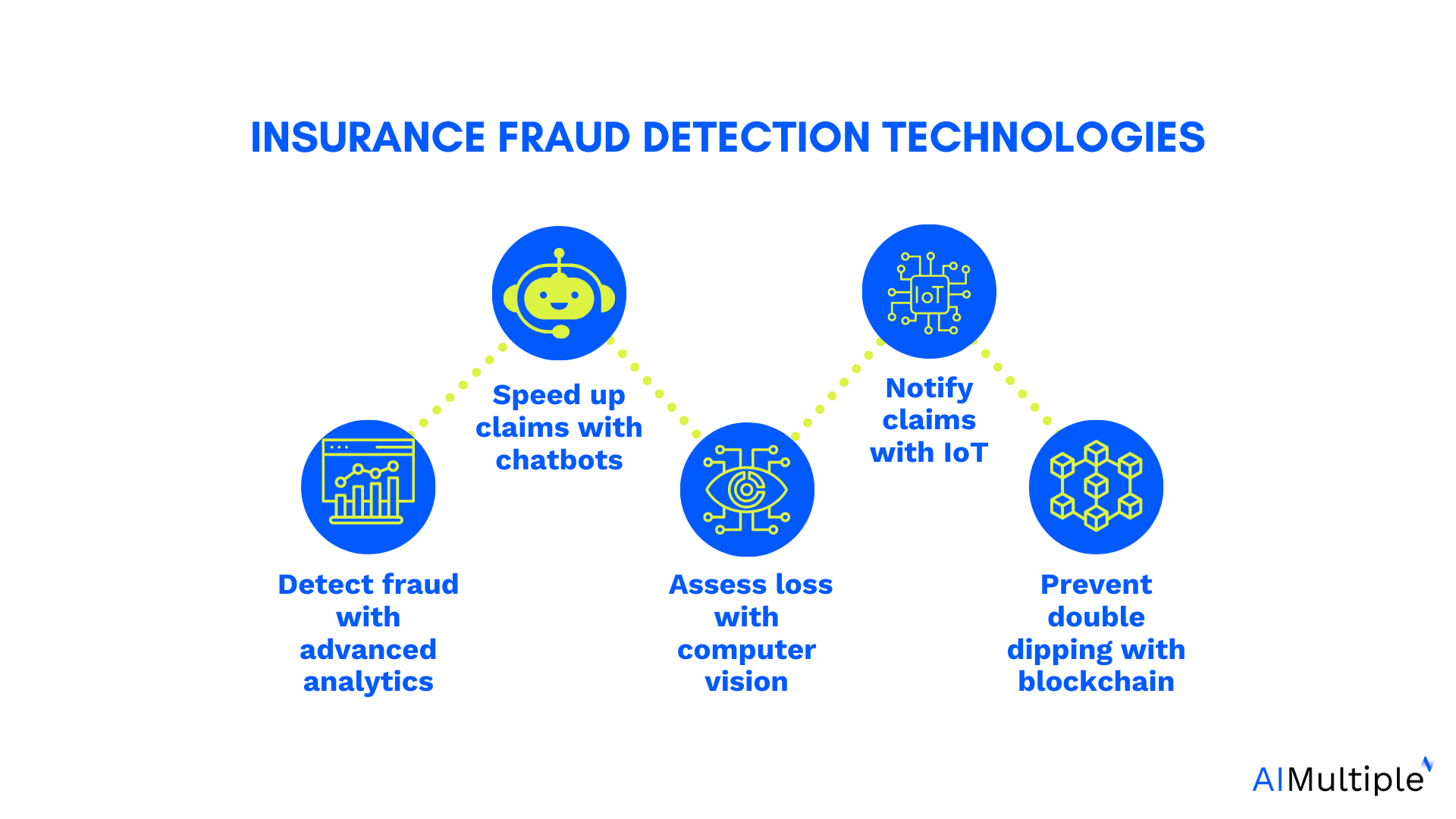
Advanced technologies improving insurance fraud detection capabilities
Data breaches in the insurance sector could have devastating consequences, potentially exposing millions of individuals to identity theft and financial fraud. Moreover, the use of AI to analyze personal behavior patterns raises questions about surveillance and the erosion of privacy rights.
The regulatory environment is struggling to keep pace with technological advancement. While frameworks like GDPR and CCPA provide some protection, the specific challenges posed by AI in insurance require more targeted regulatory responses.
Over-reliance on Automation and Loss of Human Judgment
As AI systems become more sophisticated, there’s a risk of over-reliance on automated decision-making. While AI excels at pattern recognition and data processing, it may lack the nuanced understanding and empathy that human agents bring to complex situations. This is particularly concerning in areas like claims processing, where individual circumstances may require human judgment and compassion.
The “black box” nature of many AI systems also creates challenges for transparency and accountability. When an AI system denies a claim or increases a premium, it may be difficult for both customers and insurers to understand the reasoning behind the decision. This lack of explainability can erode trust and make it difficult to identify and correct errors.
Job Displacement and Economic Impact
The automation enabled by AI inevitably raises concerns about job displacement in the insurance industry. While AI may create new types of jobs, it’s likely to eliminate many traditional roles, particularly in areas like claims processing, underwriting, and customer service. This transition could have significant economic and social impacts, particularly for workers without the skills needed for AI-enabled roles.
The industry will need to invest heavily in retraining and reskilling programs to help workers adapt to the changing landscape. However, the pace of technological change may outstrip the ability of educational and training systems to keep up.
Systemic Risks and Market Concentration
As AI systems become more prevalent and sophisticated, there’s a risk of creating new systemic vulnerabilities. If multiple insurers rely on similar AI models or data sources, a failure or bias in these systems could have widespread impacts across the industry. This concentration risk is compounded by the fact that many insurers rely on third-party AI vendors, creating potential single points of failure.
The complexity of AI systems also makes it difficult to predict and manage risks. Unlike traditional actuarial models, which are based on well-understood statistical principles, AI systems may exhibit unexpected behaviors or fail in unpredictable ways.
Regulatory Landscape and Compliance Challenges
The regulatory environment for AI in insurance is rapidly evolving, with multiple jurisdictions developing frameworks to address the unique challenges posed by these technologies. The National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC) has been at the forefront of this effort, developing principles under the acronym FACTS (Fairness, Accountability, Compliance, Transparency, and Security).
The NAIC’s 2023 Model Bulletin on AI systems requires insurers to implement comprehensive governance programs, including bias testing, consumer notifications, and third-party vendor oversight. As of 2025, 24 states have adopted this framework, creating a patchwork of regulatory requirements that insurers must navigate.
At the state level, regulations vary but generally focus on preventing discrimination and ensuring transparency. Colorado’s AI Act, effective in 2026, requires insurers to demonstrate that their AI models don’t perpetuate bias and must provide clear explanations for adverse decisions. New York’s Circular Letter No. 7 imposes similar requirements, emphasizing the need for human oversight in AI-driven decisions.
Internationally, the European AI Act and similar regulations in other jurisdictions are creating additional compliance requirements for global insurers. These regulations generally emphasize risk-based approaches, with higher-risk applications like underwriting and claims processing subject to more stringent requirements.
The Path Forward: Balancing Innovation and Responsibility
Implementing Ethical AI Frameworks
The future success of AI in insurance depends on the industry’s ability to implement ethical frameworks that balance innovation with responsibility. This requires a multi-faceted approach that includes:
Governance and Oversight: Establishing AI ethics boards and cross-functional teams to ensure accountability and transparency in AI development and deployment.
Bias Testing and Mitigation: Implementing comprehensive testing procedures to identify and address potential biases in AI systems, including regular audits and fairness assessments.
Human-in-the-Loop Systems: Maintaining human oversight for high-stakes decisions, ensuring that AI augments rather than replaces human judgment in critical areas.
Transparency and Explainability: Developing AI systems that can provide clear explanations for their decisions, enabling both customers and regulators to understand the reasoning behind automated decisions.
Investing in Talent and Skills Development
The successful integration of AI in insurance requires significant investment in human capital. This includes:
Technical Skills: Training existing employees in AI and data science skills, while recruiting new talent with expertise in machine learning, data engineering, and AI ethics.
Domain Expertise: Ensuring that AI development teams include insurance professionals who understand the nuances of risk assessment, claims processing, and regulatory requirements.
Change Management: Developing organizational capabilities to manage the cultural and operational changes that come with AI adoption.
Building Robust Data Infrastructure
The effectiveness of AI systems depends heavily on the quality and accessibility of data. Insurers need to invest in:
Data Quality Management: Implementing processes to ensure data accuracy, completeness, and consistency across all systems.
Data Integration: Breaking down data silos and creating unified data platforms that can support AI applications across the organization.
Privacy and Security: Implementing robust data protection measures that comply with regulatory requirements while enabling AI innovation.
Future Predictions: Insurance in 2030 and Beyond
Looking ahead to 2030, several trends are likely to shape the future of AI in insurance:
Predictive and Preventive Insurance Models
The industry is moving toward models that focus on preventing losses rather than simply compensating for them. AI-powered systems will continuously monitor risk factors and provide real-time recommendations to policyholders to help them avoid claims. For example, smart home systems might detect potential water damage and automatically shut off water supplies, while connected car systems might provide real-time driving feedback to prevent accidents.
Hyper-Personalized Products and Services
AI will enable the development of highly personalized insurance products that adapt in real-time to changing circumstances. Dynamic pricing models will adjust premiums based on continuous risk assessment, while personalized risk management services will provide tailored advice and interventions.
Autonomous Claims Processing
By 2030, many routine claims may be processed entirely by AI systems, from initial reporting through settlement. Computer vision systems will assess damage from photos or videos, while natural language processing will extract relevant information from claim reports and supporting documents.
New Risk Categories and Products
As AI becomes more prevalent across society, new types of risks will emerge that require insurance coverage. AI liability insurance, algorithmic bias coverage, and cyber-physical system protection are likely to become significant market segments.
Ecosystem Integration
Insurance will become more integrated with other services and platforms, with AI enabling seamless connections between insurers, healthcare providers, automotive manufacturers, and smart home systems. This ecosystem approach will enable more comprehensive risk management and better customer experiences.
The transformation of the insurance industry through AI represents both the greatest opportunity and the most significant challenge the sector has faced in decades. The potential benefits—improved efficiency, better risk assessment, enhanced customer experience, and innovative products—are substantial and compelling. However, the risks—bias and discrimination, privacy concerns, job displacement, and systemic vulnerabilities—are equally significant and demand careful attention.
The path forward requires a balanced approach that embraces innovation while prioritizing responsibility and ethical considerations. Insurers that successfully navigate this transformation will be those that invest not just in technology, but in the governance frameworks, talent development, and cultural changes necessary to deploy AI responsibly and effectively.
The regulatory landscape will continue to evolve, requiring insurers to stay agile and adaptive in their compliance approaches. The most successful companies will be those that view regulatory requirements not as constraints, but as opportunities to build trust and competitive advantage through responsible AI practices.
As we look toward 2030 and beyond, the insurance industry of the future will be fundamentally different from today’s. It will be more predictive than reactive, more personalized than standardized, and more integrated than isolated. The companies that thrive in this new landscape will be those that harness the power of AI while never losing sight of their fundamental mission: protecting people and businesses from the uncertainties of life.
The AI revolution in insurance is not a distant future possibility—it’s happening now. The question is not whether AI will transform insurance, but how quickly and responsibly this transformation will occur. The choices made today by insurers, regulators, and technology providers will determine whether this transformation creates a more equitable, efficient, and effective insurance system for all.
This blog post explores the current state and future implications of AI in the insurance industry. As technology continues to evolve rapidly, the landscape described here will undoubtedly continue to change. Stay informed about the latest developments in AI and insurance through continued research and industry engagement.
